Multiple Effect Evaporator: A Detailed Explanation of Efficient and Energy-Saving Industrial Evaporation Solutions
Release time:2026-02-02
Visits:22
In today's industrial production, energy efficiency and sustainable development have become core issues. As an efficient evaporation device, the multiple effect evaporator is playing an increasingly important role in numerous industries such as chemical engineering, pharmaceuticals, and food processing due to its excellent energy-saving characteristics and wide applicability. This article will delve into the working principle, significant advantages, potential drawbacks, main application fields, and key usage considerations of multiple effect evaporators, helping you gain a comprehensive understanding of this highly efficient and energy-saving equipment.
Working Principle of Multiple Effect Evaporators: Efficient Cascade Utilization of Thermal Energy
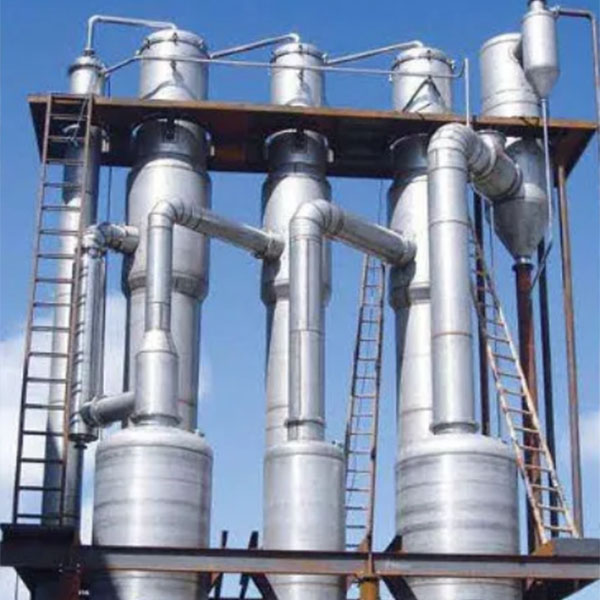

The core working principle of a
multiple effect evaporator ingeniously utilizes the thermodynamic properties of steam to achieve cascade utilization and efficient recovery of thermal energy. The basic process is as follows: First, fresh steam supplied from an external source (commonly referred to as primary steam) enters the first evaporator (called the first effect) to heat the material within, causing the water in the material to evaporate and generate secondary steam. Instead of directly discharging this secondary steam, the multiple effect evaporator introduces it into the next evaporator (the second effect) to serve as the heating steam for that effect. This process is repeated in a series of connected evaporators, with each evaporator using the secondary steam generated by the previous one as the heating medium. In this way, the initially input thermal energy is utilized multiple times, significantly improving the overall thermal energy utilization efficiency and thereby effectively reducing energy consumption.
Significant Advantages of Multiple Effect Evaporators
1. Excellent Energy-Saving Effect: This is the most core advantage of multiple effect evaporators. By repeatedly utilizing the latent heat of steam, compared to single-effect evaporators, multiple effect evaporators can significantly reduce the steam consumption per unit evaporation, thereby markedly lowering enterprises' energy costs and aligning with the development trend of energy conservation and emission reduction.
2. Compact Spatial Design: Although composed of multiple evaporators in series, multiple effect evaporators typically adopt an integrated design, resulting in a compact overall structure and relatively small footprint, facilitating layout and installation within factory workshops.
3. High Production Capacity: Multiple effect evaporators can handle large evaporation loads with high production efficiency, meeting the requirements for continuous and stable material concentration or separation in industrial production.
4. Relatively Simple Operation Process: With rational design and the assistance of automatic control, the daily operation of multiple effect evaporators is relatively straightforward and easy to achieve stable control.
Potential Disadvantages of Multiple Effect Evaporators
1. High Initial Equipment Investment: The equipment structure of multiple effect evaporators is relatively complex, including multiple evaporator units and auxiliary equipment, so their initial purchase and installation costs are relatively high. Generally, the more effects there are, the higher the initial investment.
2. Relatively Complex System Operation: Due to the collaborative operation of multiple effects, it is necessary to precisely control multiple parameters such as temperature, pressure, and liquid level of each effect to ensure stable operation and efficient energy saving of the entire system, which places certain requirements on the skill level of operators.
3. High Maintenance Requirements: The complexity of the equipment structure also means that maintenance work is relatively complex, requiring professional technical personnel to conduct regular inspections, cleaning, and repairs to ensure long-term stable operation of the equipment.
Wide Application Fields of Multiple Effect Evaporators
Multiple effect evaporators, with their efficient and energy-saving characteristics, have been widely applied in various industrial fields:
Chemical Industry: Commonly used in processes such as concentration, crystallization, and solvent recovery of various solutions, for example, in the production of salts, organic acids, and inorganic compounds.
Pharmaceutical Industry: Plays an important role in links such as concentration, purification, drying of liquid medicines, and preparation of traditional Chinese medicine extracts, ensuring drug quality and active ingredients.
Food Industry: Applied in the concentration, dehydration, and drying of foods such as fruit juices, jams, dairy products, sugar, and starch sugar, retaining food flavor and nutritional components.
Seawater Desalination: As one of the core equipment for seawater desalination, it converts seawater into fresh water through evaporation and condensation processes.
High-Salinity Wastewater Treatment: For high-salinity, high-concentration organic wastewater generated in industrial production, multiple effect evaporators can achieve evaporation separation of water and concentration crystallization of salts, achieving wastewater volume reduction and resource utilization.
Precautions for Using Multiple Effect Evaporators
To ensure the safe, efficient, and stable operation of multiple effect evaporators, the following points should be noted during use:
1. Accurate Matching of Material Properties: Based on the properties of the material to be processed, such as viscosity, corrosivity, thermal sensitivity, and scaling tendency, select the appropriate type of evaporator (such as rising film, falling film, forced circulation, etc.) and suitable operating parameters.
2. Reasonable Selection of Number of Effects: Increasing the number of effects can improve energy-saving effects but also increases equipment investment and operational complexity. The most appropriate number of effects should be selected through comprehensive consideration of actual production needs, material properties, energy costs, and investment returns.
3. Refined Operational Control: Strictly control key parameters such as heating steam pressure, temperature, feed rate, discharge concentration, and vacuum degree (if vacuum operation is adopted) of each effect to ensure balanced and stable operation between effects and prevent problems such as dry walls and scaling.
4. Regular Maintenance: Develop and implement a comprehensive maintenance plan, including regular cleaning of heat exchange surfaces to prevent scaling, inspection of sealing performance, lubrication of rotating parts, and calibration of instruments, to promptly identify and solve potential faults and extend the service life of the equipment.
Summary
Multiple effect evaporators are undoubtedly an efficient and energy-saving evaporation technology equipment in modern industrial production. Through its ingenious design for cascade utilization of thermal energy, it significantly reduces energy consumption while possessing high production efficiency and wide applicability. Although it has characteristics such as high initial investment and relatively complex operation and maintenance, from the perspective of long-term energy savings and production efficiency, multiple effect evaporators are still an ideal choice for many industries. In practical applications, users should fully understand their own needs, select models rationally, and pay attention to standardized operation and maintenance to give full play to the advantages of multiple effect evaporators and create greater value for enterprises."