
PRODUCTS
CONTACT US
+86-13706172093PRODUCTS
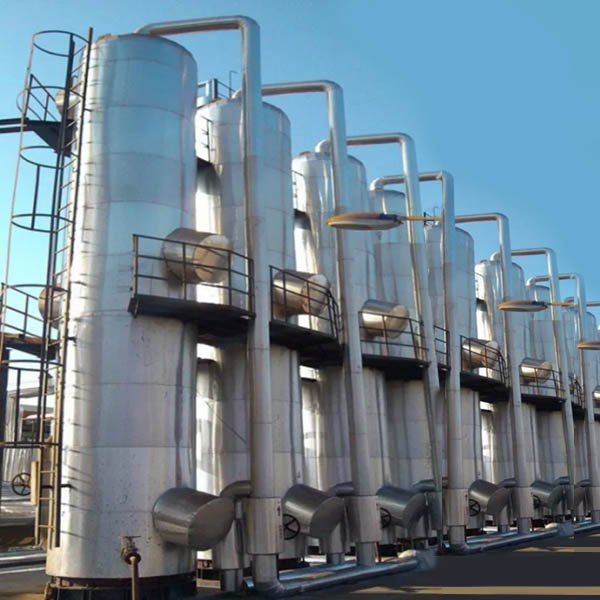
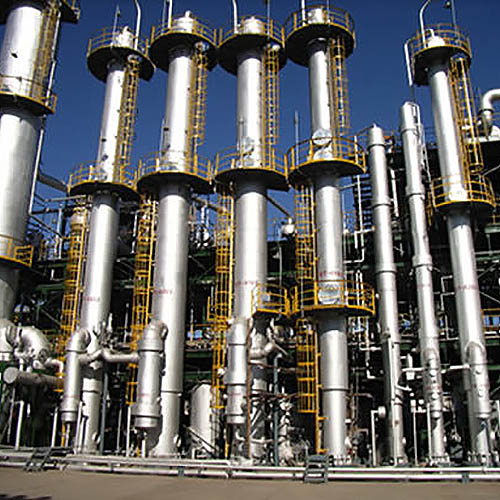
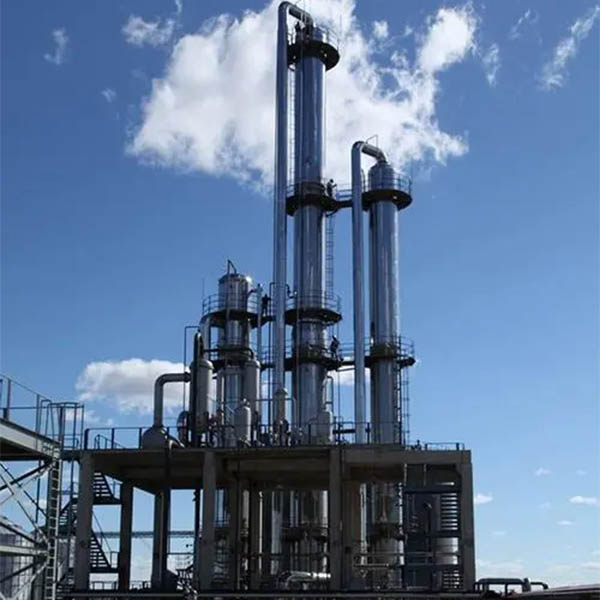
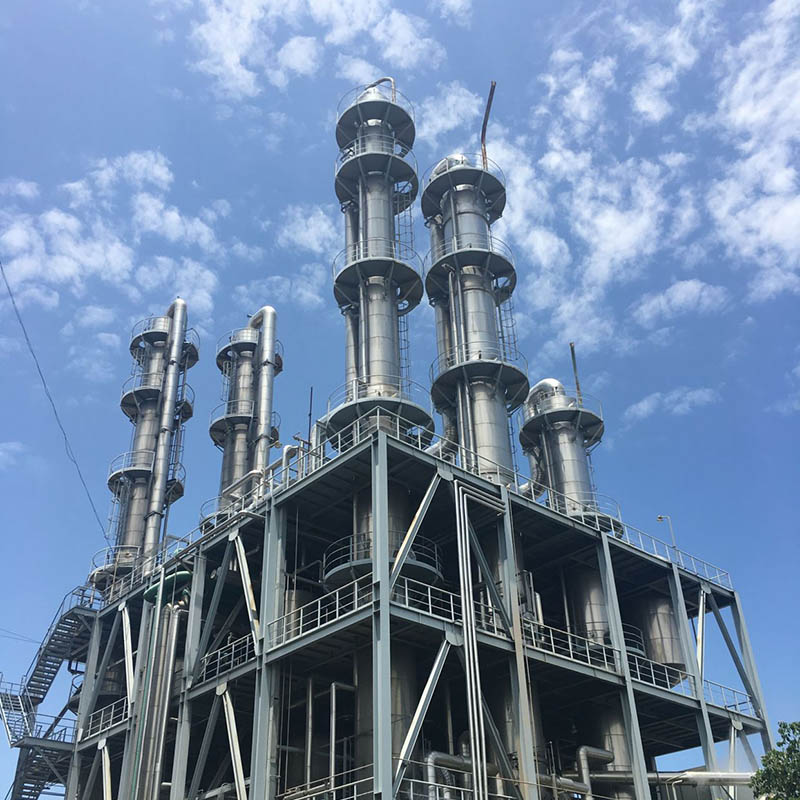
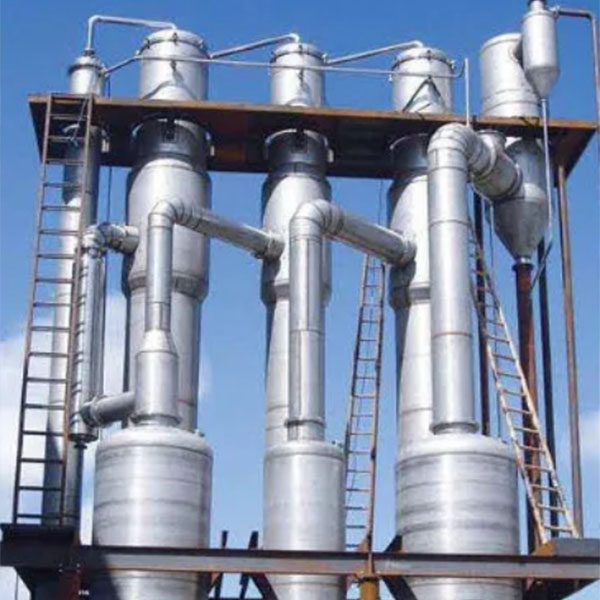
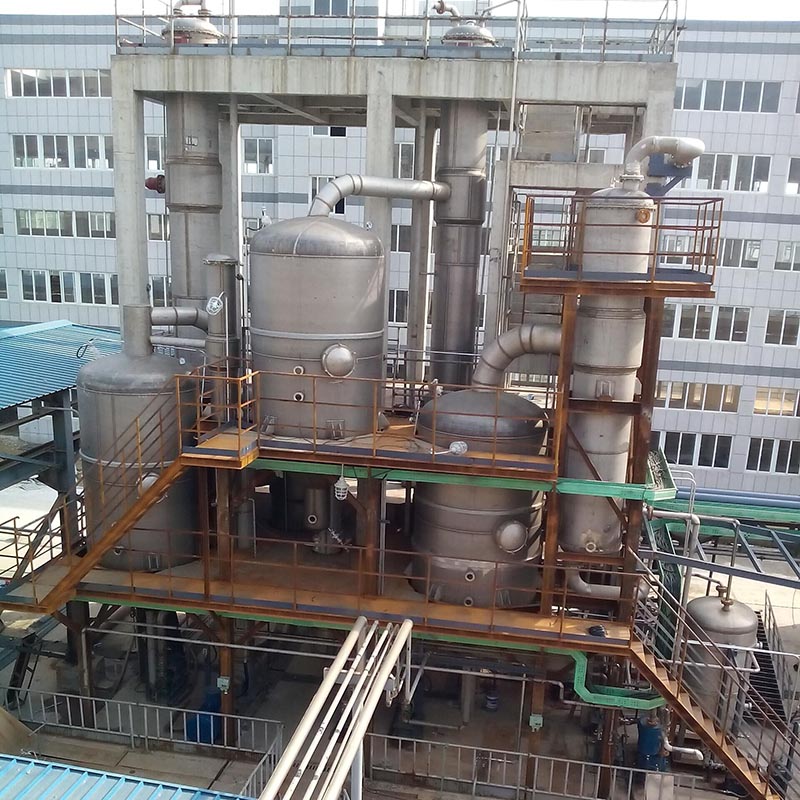
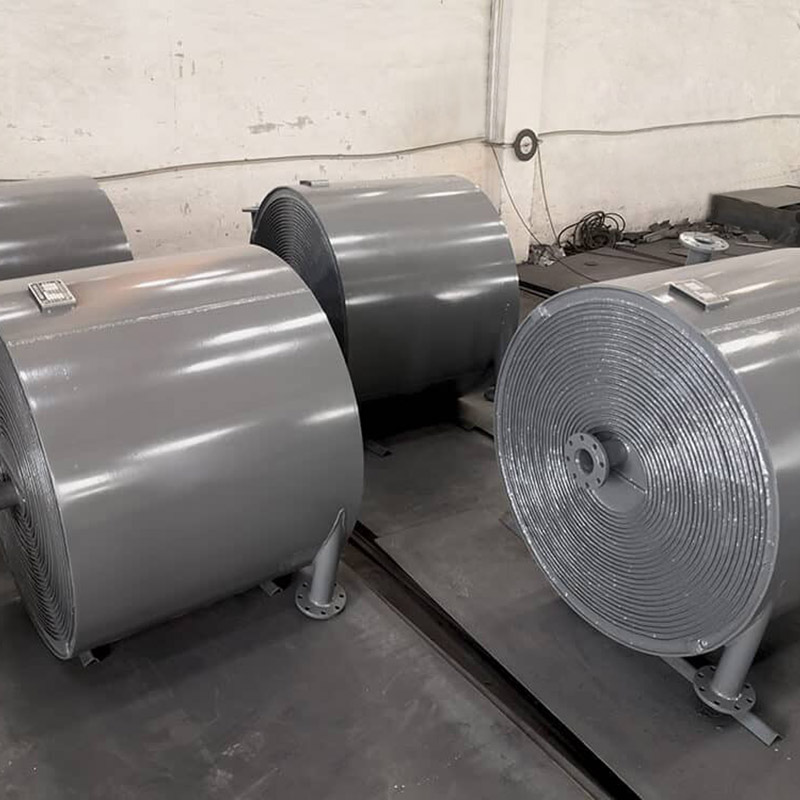








Wuxi Hongdinhua Chemical Equipment Co.,Ltd.is mainly engaged in researching, developing, designing and manufacturing metal pressure vessel used in Petrochemical industry, pharmaceutical, fine chemical, photoelectric, solar technology, new energy technology, environmental technology.
Research, develop, design, and manufacture metal pressure vessels
Wuxi Hongdinhua Chemical Equipment Co.,Ltd. Was established in the year of 2010 with registered capital of 10.8 miliion yuan (CNY). Wuxi Hongdinhua Chemical Equipment Co.,Ltd.is mainly engaged in researching, developing, designing and manufacturing metal pressure vessel used in petrochemical industry, pharmaceutical, fine chemical, photoelectric ...
More >
professional manufacturer
Rich industry experience
 On time delivery
On time delivery
convenient transportation
Strict testing before leaving the factory
Follow us to stay informed about industry trends

Heat Exchangers: Analysis of Principles, Types, and Wide Applications
Heat exchangers are indispensable key equipment in modern industry and daily life. They efficiently transfer thermal energy between different fluids through scientific heat transfer methods. Whether it is temperature control in industrial production or comfortable environment regulation in daily life, heat exchangers play a crucial role. This article will delve into the basic principles, common types, and wide application fields of heat exchangers. What is a Heat Exchanger? Simply put, a heat exchanger is a specially designed device used to transfer heat between two or more fluids of different temperatures, and these fluids are usually physically isolated from each other. Its core purpose is to achieve effective heat transfer, thereby heating, cooling, or maintaining the temperature of a specific fluid. Heat exchangers are used in various industries and are key equipment for improving energy efficiency and reducing energy consumption. Working Principle of Heat Exchangers The operation of heat exchangers is based on the three basic principles of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. In practical applications, these three heat transfer methods often exist simultaneously, but one or two of them are dominant. Heat is always transferred from the high...
2026-03-09
Thin-Film Evaporators: Principles, Applications and Market Prospects Analysis
Working Principles of Thin-Film Evaporators Thin-film evaporators (TFEs) operate on the core principle of forming a thin liquid film on a heated surface to maximize heat transfer efficiency and minimize material residence time. The evaporation process relies on the large heat transfer area per unit volume of the thin film and the high turbulence of the fluid, enabling rapid vaporization of volatile components. The working process consists of four key steps: 1. Feed Distribution Raw material (liquid or viscous fluid) is pumped into the top of the evaporator and uniformly distributed onto the inner surface of the heated cylindrical shell via a specialized distributor. The distributor ensures the feed spreads into a continuous, thin film with a thickness typically ranging from 0.1 to 1 mm, avoiding localized pooling that would reduce heat transfer efficiency. 2. Thin-Film Formation The film formation is driven by one of two mechanisms, depending on the TFE type: - Gravity-driven formation: For falling-film evaporators, the liquid film flows downward along the heated wall under gravity, with turbulence enhanced by the downward flow velocity. - Mechanical-driven formation: For wiped-film evaporators, rotating wiper blades or scrapers spread the liquid into a thin fi...
2026-03-06

Evaporative Crystallizers: Working Principles, Technical Characteristics and Industrial Applications
Working Principles of Evaporative Crystallizers Evaporative crystallizers achieve solid-liquid separation by removing solvents from solutions through thermal evaporation, increasing solute concentration to reach a supersaturated state, and inducing the formation and growth of solid crystals. The entire process consists of four interconnected stages: 1. Feed Pretreatment Raw solutions (e.g., industrial wastewater, chemical reaction liquors, ore leachates) undergo filtration, pH adjustment, and scale inhibition treatment first. Filtration removes suspended solids that may interfere with crystal growth or block equipment; pH adjustment optimizes the solution environment to prevent the formation of insoluble impurities; anti-scaling agents are added to avoid the deposition of mineral salts on heat exchange surfaces, ensuring stable operation of the crystallizer. 2. Evaporation and Concentration Pretreated solutions are pumped into the crystallizer’s heat exchange zone, where they are heated by a heat source (steam, thermal oil, or industrial waste heat). Most evaporative crystallizers operate under vacuum conditions, which lowers the solvent’s boiling point, reduces energy consumption, and prevents thermal decomposition of heat-sensitive solutes. As the solvent vap...
2026-03-02

Wastewater Evaporators: Working Principles, Core Types and Environmental Applications
Working Principles of Wastewater Evaporators Wastewater evaporators realize the separation of water and contaminants in wastewater through thermal-driven phase transition, converting liquid water into vapor while concentrating solid or dissolved pollutants for centralized treatment. The core process involves four key steps: 1. Wastewater Pretreatment Raw wastewater is first subjected to filtration, pH adjustment, and scale inhibition treatment to remove large suspended solids, adjust the water quality to a suitable range, and prevent scaling or corrosion of the evaporator’s heat exchange surface. For high-salt wastewater, anti-scaling agents are added to avoid crystal deposition that could block pipelines and reduce heat transfer efficiency. 2. Heating and Vaporization Pretreated wastewater is pumped into the evaporator’s heat exchange chamber, where it is heated by a heat source (e.g., steam, thermal oil, industrial waste heat) to a temperature above its boiling point under the operating pressure. Most industrial wastewater evaporators adopt vacuum operation technology, which lowers the boiling point of wastewater to 40–70℃, significantly reducing energy consumption and avoiding thermal decomposition of organic pollutants. During heating, water molecules...
2026-02-27

CONTACT US
Not sure which product is suitable for you? Let our knowledgeable sales team guide you in choosing the most suitable solution for your needs.