Tubular Heat Exchangers: The Efficient Core Equipment for Industrial Heat Exchange | Detailed Explanation of Working Principles and Applications
Release time:2026-01-30
Visits:24
In industrial production, heat transfer is a crucial link in maintaining process stability and improving production efficiency. As a widely used heat exchange device, the tubular heat exchanger, with its efficient heat transfer performance and stable operational capability, has become an indispensable core equipment in multiple industries such as chemical engineering, petroleum, and pharmaceuticals. This article will comprehensively analyze the industrial value of tubular heat exchangers from working principles, structural composition, core advantages to application fields.
Working Principle of Tubular Heat Exchangers: Synergy of Heat Conduction and Hydrodynamics
The core function of a
tubular heat exchanger is to realize heat transfer between two fluids of different temperatures, and its working principle is based on the basic laws of heat conduction and hydrodynamics. Simply put, when two fluids with different temperatures flow inside the equipment, heat is transferred from the high-temperature fluid to the low-temperature fluid, and the tubular heat exchanger makes this process efficient and controllable through a special structural design.
Specifically, there are two fluid channels in a tubular heat exchanger: one is the ""tube-side fluid,"" which flows through the tubes inside the equipment; the other is the ""shell-side fluid,"" which flows in the annular space between the outside of the tubes and the shell. Due to the temperature difference between the two fluids, heat is transferred from the high-temperature fluid to the low-temperature fluid through the tube wall (i.e., the ""heat conduction bridge""). At the same time, the flow state of the fluid (such as flow velocity and direction) directly affects the heat transfer efficiency—by optimizing the fluid flow parameters, heat loss can be further reduced and energy utilization efficiency can be improved.
Structural Composition of Tubular Heat Exchangers: From Core Components to Overall Design
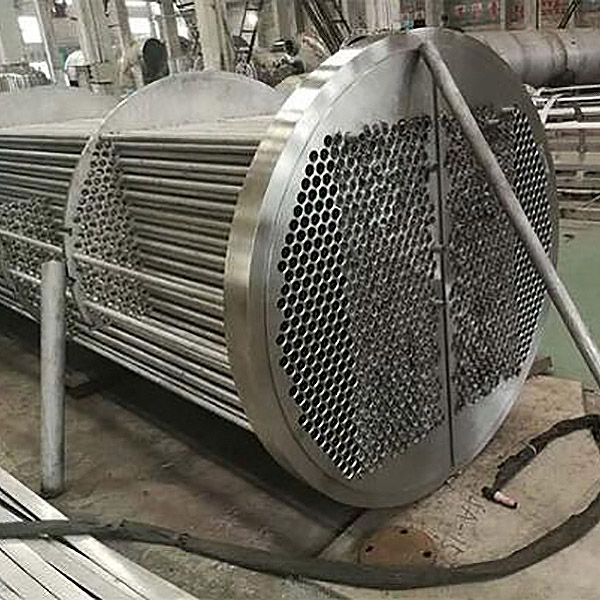
The stable operation of a tubular heat exchanger relies on precise structural design. It is mainly composed of three core components: tube bundle, shell, and tube sheet. These components work together to ensure efficient and safe heat transfer.
- Tube Bundle: As the core component for heat transfer, the tube bundle is composed of multiple parallel tubes and serves as the flow channel for the tube-side fluid. The material and arrangement of the tubes (such as inline or staggered arrangement) directly affect the heat transfer area and the degree of fluid disturbance, thereby influencing the overall heat transfer efficiency.
- Tube Sheet: Located at both ends of the heat exchanger, it is used to fix the tube bundle and also plays the role of separating the tube-side and shell-side fluids, ensuring that the two fluids do not mix and guaranteeing operational safety.
- Shell: As the outer structure of the equipment, the shell provides a flow space for the shell-side fluid, protects the internal components, and bears the pressure and temperature loads during operation.
The combination of these components not only realizes the separation and flow of fluids but also further enhances the heat transfer effect through structural design (such as baffles guiding the flow direction of the shell-side fluid), making heat transfer more uniform and efficient.
Core Advantages of Tubular Heat Exchangers: Efficiency, Stability, and Wide Applicability
The reason why tubular heat exchangers can occupy an important position in the industrial field is closely related to their unique advantages:
1. Efficient Heat Transfer Performance
By optimizing the tube bundle arrangement, tube size (diameter, length), and fluid flow rate, tubular heat exchangers can significantly improve the heat transfer coefficient, reduce the equipment volume required for unit heat transfer, and meet the demand for rapid and efficient heat exchange in industrial production.
2. Strong Structural Strength and Sealing Performance
The overall design of the equipment fully considers the complexity of the industrial environment. The shell and tube sheet are made of high-strength materials, combined with a precise sealing structure, enabling it to operate stably in high-pressure, high-temperature, and even corrosive environments, ensuring the safety and continuity of the production process.
3. Flexible Adaptation to Different Process Requirements
Whether heating, cooling, condensation, or evaporation is needed, tubular heat exchangers can adapt to the temperature control requirements of different processes by adjusting fluid parameters (such as flow rate, temperature) and structural design (such as multi-pass design), with wide applicability.
Application Fields of Tubular Heat Exchangers: Multi-Industry Coverage in Industrial Scenarios
With its efficient, stable, and flexible characteristics, tubular heat exchangers have become ""standard"" equipment in multiple industrial fields:
- Chemical Industry: Used for heating or cooling in reaction processes, such as temperature control in synthesis reactions and solution concentration;
- Petroleum Industry: Realizes heat recovery and utilization in crude oil processing and refining processes, reducing energy consumption;
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Used in key links such as constant temperature reactions and material sterilization in drug production to ensure product quality;
- Metallurgical Industry: Performs cooling or heating during metal smelting and rolling processes to maintain stable process temperatures.
In addition, tubular heat exchangers also play an important role in food processing, electric power, environmental protection, and other fields, becoming the core equipment for heat management in industrial production.