Analysis of Evaporation Equipment Types and Application Guide: How to Efficiently Select Suitable Industrial Equipment
Release time:2025-10-15
Visits:337
Evaporation equipment is the core device for solution concentration, crystallization, or solvent separation in industrial production. It removes solvents through the evaporation process and is widely used in industries such as chemical engineering, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and environmental protection. This article will provide readers with comprehensive application guidance from three aspects: equipment types, selection key points, and industry trends.
I. Mainstream Evaporation Equipment Types and Characteristics
1. MVR Evaporator (Mechanical Vapor Recompression Evaporator)
The MVR evaporator uses a mechanical compressor to pressurize and heat the secondary steam for recycling, significantly reducing energy consumption. It is suitable for high - salt wastewater treatment, biopharmaceuticals, and chemical production. For example, in chemical wastewater treatment, its energy - saving efficiency is over 40% higher than that of traditional evaporation technologies, and it reduces the reliance on additional heat sources.
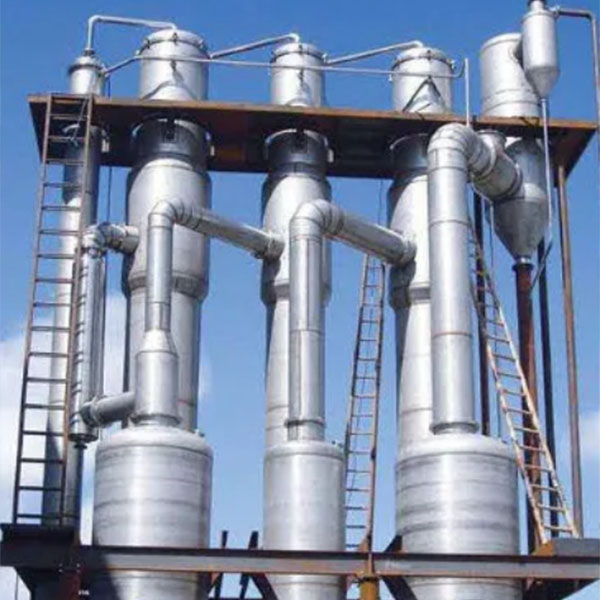
2. Multi - effect Evaporator
The multi - effect evaporator uses the steam generated in the previous effect to heat the subsequent units by connecting multiple evaporation units in series, which is suitable for large - scale concentration scenarios. Designs such as double - effect and triple - effect can further improve thermal energy utilization. It is commonly used in food processing (such as juice concentration) and the pharmaceutical industry.
3. Rotary Evaporator
This type of equipment increases the surface area of the solution by rotating the evaporation flask to accelerate solvent volatilization. It is suitable for solvent recovery and sample concentration in laboratories and small - scale production. It is easy to operate and highly controllable, and is often used in the purification of pharmaceutical intermediates and scientific research.
4. Forced - circulation Evaporator
For high - viscosity, easily crystallized, or easily scaled liquids, the forced - circulation evaporator drives the solution to circulate through a pump, avoiding problems such as local overheating or deposition. It is suitable for scenarios such as the concentration of chemical intermediates and the production of syrup.
The thin - film evaporator forms a thin layer of the solution on the heating surface, improving heat transfer efficiency and reducing the risk of decomposition of heat - sensitive substances. Its processing capacity ranges from dozens of liters to thousands of liters per hour, and it is suitable for the extraction of active ingredients in the pharmaceutical industry and the concentration of heat - sensitive food materials.
II. Key Considerations for Evaporation Equipment Selection
1. Solution Characteristics
Select the equipment material and working mode according to the viscosity, heat sensitivity, corrosiveness, and scaling tendency of the solution. For example, the thin - film evaporator is more suitable for heat - sensitive materials due to its low - temperature and rapid evaporation; stainless steel or alloy materials can handle corrosive solutions.
2. Processing Capacity and Energy Efficiency
Large - scale industrial production (such as wastewater treatment) tends to choose multi - effect or MVR evaporators for large - scale energy savings; for small - and medium - scale processing, rotary evaporators or single - effect thin - film evaporators can be selected.
3. Operating Conditions and Automation Requirements
Vacuum operation can lower the boiling point and reduce energy consumption, which is commonly used in the processing of heat - sensitive materials. In addition, modern equipment is often equipped with automatic temperature control and cleaning systems, which helps to stabilize production and reduce maintenance costs.
4. Balance between Environment and Economy
Comprehensively evaluate equipment investment, operating costs, and environmental protection requirements. For example, although the initial investment in MVR technology is high, it can significantly reduce energy costs and carbon emissions in the long - term operation.
III. Industry Application Trends and Technological Developments
1. Popularization of Energy - efficient Technologies
Energy - saving technologies represented by MVR and multi - effect evaporation are gradually replacing traditional single - effect equipment, especially becoming the focus of industrial upgrading under the "dual carbon" goal.
2. Intelligent and Modular Design
Evaporation equipment integrated with sensors and Internet of Things technology can achieve remote monitoring and fault warning, while modular design shortens the installation cycle to meet the demand for rapid production.
3. Innovation in Green Processes
Combining low - temperature evaporation and high - efficiency condensation technologies reduces the emission of volatile organic compounds, meeting the strict environmental protection standards of the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
In summary, the selection of evaporation equipment should be guided by process requirements, comprehensively considering technological adaptability and economy. In the future, with breakthroughs in new materials and intelligent control technologies, the evaporation process will develop towards lower energy consumption and higher precision.