Thin Film Evaporator: Principle, Application, and Market Prospect Analysis
Release time:2025-09-24
Visits:317
As an indispensable and highly efficient separation device in modern industry, the thin film evaporator has become a core equipment in fields such as chemistry, biopharmaceuticals, and food processing, thanks to its unique working principle and wide range of application scenarios. By precisely controlling temperature and vacuum degree, this device can achieve rapid concentration, desolvation, and purification of solutions. While improving production efficiency, it significantly preserves the active ingredients of materials, and is especially suitable for the processing needs of heat - sensitive and high - viscosity materials.
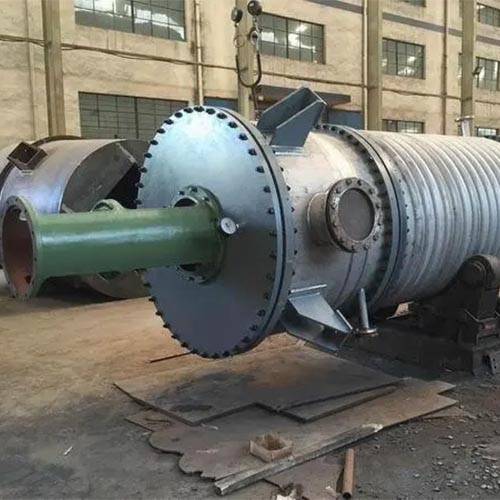
I. Technical Principle and Structural Design
The core working principle of the thin film evaporator is based on the synergistic effect of an ultra - thin liquid film (0.5 - 2mm) formed by the material on the heating surface and the vacuum system. During operation, the material enters the evaporation chamber from the top, and the rotating scraper system evenly distributes it on the heating surface, forming a continuously updated dynamic liquid film. Under vacuum decompression conditions, the boiling point of the solvent decreases. Combined with the heating of an external heat source (such as steam or heat - conducting oil), the solvent evaporates rapidly and enters the condensation system, ultimately achieving efficient separation.
The device usually adopts a vertical or horizontal structure. The core components include a rotating shaft, scrapers, an evaporation chamber, a jacket heating device, and a precise temperature control system. The optimized mechanical design shortens the material residence time to 5 - 60 seconds, effectively avoiding the decomposition of heat - sensitive components. Some advanced models can also precisely control the evaporation rate and separation accuracy by adjusting the scraper rotation speed and direction.
II. Core Advantages and Performance Characteristics
1. High - efficiency heat transfer and low energy consumption: The scraper - forced film - forming technology greatly improves the heat transfer efficiency, with an evaporation intensity of up to 200kg/(m²·h), saving more than 40% energy compared with traditional evaporation equipment. Low - temperature operation in a vacuum environment further reduces energy consumption.
2. Wide material adaptability: It can handle liquids with a viscosity range of up to 100,000 centipoise and shows excellent stability for materials containing particles, prone to crystallization, or foaming. For example, in the purification of epoxy resin, the thin film evaporator can increase the product purity to 99.9%, solving the coking problem of traditional processes.
3. Precise process control: The closed - type continuous production mode, combined with an automated control system, can monitor the liquid film thickness, temperature, and vacuum degree in real - time, ensuring the consistency of product quality.
4. Easy maintenance and cleaning: The modular design simplifies the disassembly process. The special surface treatment process (such as mirror polishing) reduces the risk of scaling, and the maintenance cost is significantly reduced.
III. Application Cases in Multiple Fields
- Pharmaceutical industry: It is used for the concentration of polypeptide intermediates, liposomes, and traditional Chinese medicine extracts. The removal efficiency of organic solvents is over 98%, while maintaining the active ingredients of drugs (e.g., the retention rate of vitamins is increased by 20%).
- Food processing: Low - temperature concentration (below 60°C) of fruit juice and honey can increase the solid content concentration from 12°Brix to 65°Brix, with a vitamin C loss rate of less than 5%.
- Chemical and environmental protection: It processes high - viscosity materials such as high - molecular polymers and epoxy resins, achieving a solvent recovery rate of over 95%. In the purification of lithium - battery electrolyte and the refining of biodiesel, the separation accuracy of the device reaches 99.5%.
- New material R & D: It supports the solvent removal and crystallization processes of high - end materials such as graphene composites and organosilicon, helping the product purity to exceed 99.99%.
IV. Technological Innovation and Market Trends
With the advancement of Industry 4.0, the thin film evaporator is evolving towards intelligence and energy conservation:
- Intelligent control system: By integrating Internet of Things sensors and AI algorithms, it realizes the dynamic optimization of evaporation parameters, and the equipment production capacity is increased by 30%.
- Green and energy - saving technology: Using MVR (Mechanical Vapor Recompression) technology, the secondary steam recycling rate reaches 80%, and carbon emissions are reduced by more than 60%. After the upgrade, a pharmaceutical enterprise achieved an annual emission reduction of 8000 tons.
- Application of new materials: Graphene - coated heating tubes increase the heat conduction efficiency by 50%, extend the equipment service life to 15 years, and significantly reduce the maintenance frequency.
V. Future Market Potential
The global thin
film evaporator market is expected to grow at an average annual rate of 6.5%. The driving factors include the expansion of the biopharmaceutical industry, the surging demand for new energy materials, and the promotion of environmental protection policies. The Asia - Pacific region has become the fastest - growing market. Especially in the modernization of traditional Chinese medicine and the upgrading of the food industry, the penetration rate of the equipment will continue to increase.
In summary, through technological innovation and cross - field applications, the thin film evaporator is reshaping the landscape of modern industrial separation technology. Its characteristics of high efficiency, precision, and energy conservation will continue to promote industrial upgrading and open up broader development space.