Analysis of the Working Principle, Core Types and Environmental Protection Applications of Wastewater Evaporators
Release time:2025-09-17
Visits:345
Overview of Wastewater Evaporators
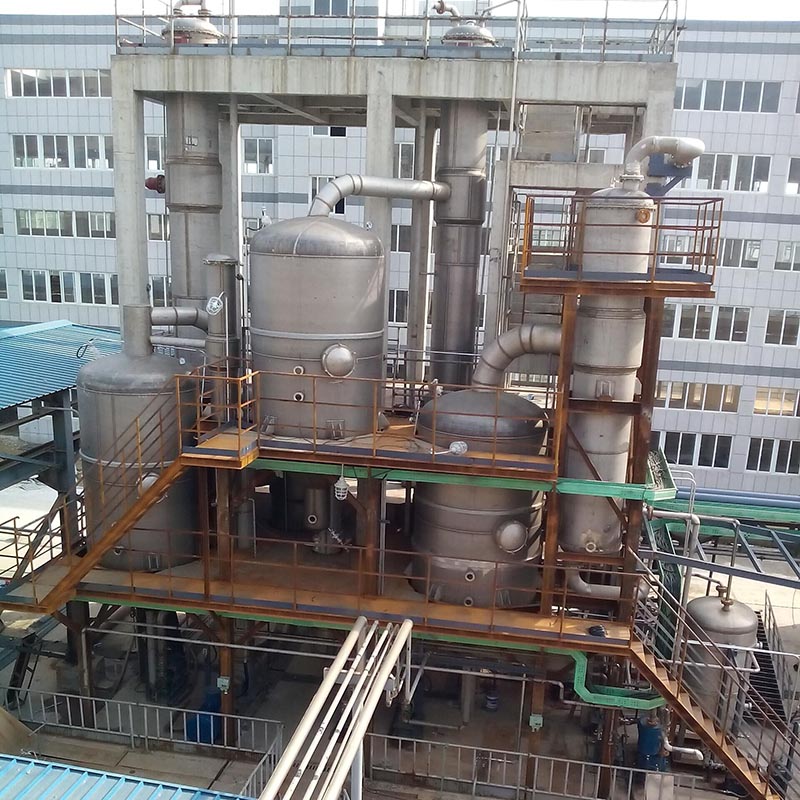
Wastewater evaporators are key environmental protection equipment for treating industrial wastewater with high salt and high organic matter content. They are widely used in industries such as chemical engineering, pharmaceuticals, food, and fermentation. The core principle is to separate salts, organic matter, and water in wastewater through evaporation and concentration technology, achieving standard - compliant discharge and resource recovery. Compared with traditional treatment methods, wastewater evaporators have advantages such as high efficiency, energy - saving, small footprint, and strong adaptability.
I. Working Principle and Technological Upgrades
Wastewater evaporators heat the wastewater to vaporize the water, thereby concentrating the waste liquid and separating impurities. Traditional evaporators rely on a single heat source, while modern technology combines multi - effect evaporation and mechanical vapor recompression (MVR) technology. For example:
1. Multi - effect evaporation: By connecting multiple evaporation units in series, the secondary steam is reused, and energy consumption can be reduced by 30% - 50%. The concentration ratio of a four - effect evaporator can reach 10% - 15%, which is suitable for large - scale treatment of high - salt wastewater.
2. MVR evaporation technology: A steam compressor is used to increase the temperature of the low - temperature secondary steam, which serves as a circulating heat source. The energy consumption is only 15 - 100 kW·h per ton of water, and the operating cost is only 1/8 - 1/2 of that of traditional evaporators.
In addition, low - temperature evaporation technology (operating temperature of 35 - 50°C) breaks through the high - temperature limitation and can efficiently treat organic waste liquids and oily wastewater. Experimental data shows that its COD removal rate exceeds 90%, and the ammonia - nitrogen removal rate is as high as 95%. It is especially suitable for sensitive waste liquids such as landfill leachate.
II. Core Types and Applicable Scenarios
According to structural and technological differences,
wastewater evaporators are divided into the following categories:
1. Classified by the number of effects:
- Single - effect evaporator: Suitable for small - scale and intermittent treatment. It is simple to operate but has relatively high energy consumption.
- Multi - effect evaporators (double - effect, triple - effect, four - effect): Through multi - stage heat energy recovery, the treatment capacity can reach 1 - 30 tons per hour, taking into account both efficiency and economy.
2. Classified by operating mode:
- Forced - circulation type: Suitable for waste liquids with high viscosity and easy to scale. The pump is used for forced circulation to avoid coking on the tube wall.
- Thin - film evaporators (rising - film, falling - film, rotating thin - film): A liquid film is formed through high - speed rotation, and the evaporation speed is increased by more than 50%. It is especially suitable for heat - sensitive materials. The rotating thin - film technology operates in a vacuum environment, reducing the footprint by 40%. It can also treat waste gas simultaneously to avoid secondary pollution.
3. Thermal - driven type:
- Steam compressor evaporator: Integrated with PLC automatic control, it can operate continuously for 24 hours. After biochemical treatment, the condensed water meets the reuse standard.
III. Technological Advantages and Environmental Protection Value
1. Efficient energy utilization: Through multi - effect series connection and steam recompression, energy consumption is reduced by 80% compared with traditional processes, and the heat energy recovery rate exceeds 70%.
2. Significant waste liquid reduction: The volume of wastewater can be reduced by 80% - 90%. The concentrated liquid can be dried for recovery or incinerated, realizing the resource utilization of solid waste.
3. Guarantee of standard - compliant discharge: After treatment, the indicators such as COD and TDS of the condensed water are significantly reduced, meeting the requirements of the "Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard".
4. Automation and adaptability: The modular design supports customized transformation. The automatic control system reduces manual intervention and is suitable for wastewater with different concentrations and compositions.
IV. Industry Applications and Future Trends
Wastewater evaporators have been maturely applied in fields such as coal chemical industry, petroleum refining, and pharmaceutical manufacturing. For example:
- Treatment of high - salt wastewater: Crystalline salts such as sodium chloride and sodium sulfate are separated, and their purity reaches the industrial - grade standard.
- Recovery of organic solvents: For waste liquids from pesticides and dyes, solvent regeneration and harmless treatment of toxic substances are achieved.
In the future, with the iteration of thin - film technology, low - temperature evaporation, and intelligent control systems, the equipment will develop towards lower energy consumption and broader adaptability, providing core support for the green transformation of industries.