Horizontal Storage Tanks: Structural Features, Application Fields, and Selection Guide
Release time:2025-11-05
Visits:301
Horizontal storage tanks are horizontally placed cylindrical sealed containers primarily used for storing liquid or gaseous media. They are widely employed in dozens of industries such as chemical, petroleum, food, environmental protection, fire protection, and pharmaceuticals. Their design takes both functionality and safety into account, capable of meeting storage requirements under high - temperature, high - pressure, and complex chemical environments.
I. Core Features and Material Selection
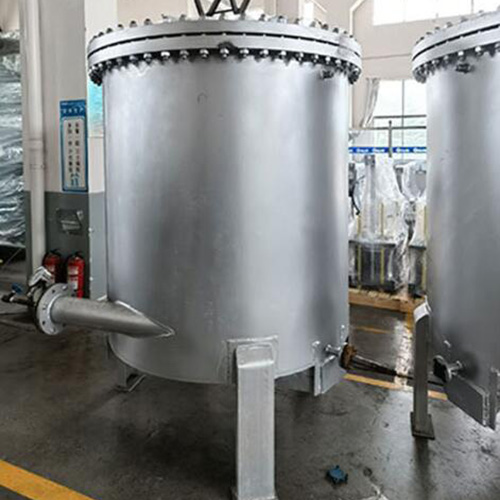
The volume of horizontal storage tanks is flexible, usually less than 100 cubic meters and no more than 150 cubic meters at maximum. However, in customized scenarios, larger capacities can be achieved through on - site assembly and welding. The tank body materials are often polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), stainless steel, or steel - lined plastic composite materials with excellent corrosion resistance. Among them, all - plastic tanks made by rotational molding are the mainstream choice due to their high cost - effectiveness and strong chemical corrosion resistance; stainless - steel tanks are suitable for fields with high hygiene requirements such as food and medicine.
II. Structural Design and Pressure Adaptability
The tank body structure can be divided into two types: flat end - caps and dished end - caps. The flat end - cap design can withstand an internal pressure of 40 kPa, while the dished end - cap can tolerate an internal pressure of 0.2 MPa, meeting the requirements of different pressure scenarios. Above - ground storage tanks usually adopt a double - saddle support structure, while underground storage tanks need to be equipped with angle - steel reinforcement rings to enhance stability. The circumferential welds use the lap - joint process, and the longitudinal welds use the butt - joint process. The end - caps are connected to the tank wall through alternately arranged ring plates to ensure sealing and durability.
III. Classification of Application Scenarios
1. Above - ground Horizontal Storage Tanks: Used for storing media such as gasoline and liquefied petroleum gas, they are commonly found in gas stations or production workshops, facilitating transportation and daily maintenance.
2. Underground Horizontal Storage Tanks: Buried underground to reduce the floor area and stabilize the temperature and pressure of the media. They are mostly used for scenarios where media such as fire - fighting water and crude oil need to be stored away from light or at low temperatures.
3. Semi - underground Horizontal Storage Tanks: Positioned between above - ground and underground, they combine safety and operational convenience and are suitable for storing materials such as vegetable oils and chemical solvents.
IV. Key Points for Selection and Installation
1. Foundation Design: Select revetment - type, ring - wall - type, or outer - ring - wall - type foundations according to geological conditions. Soft soil layers need to be pre - reinforced.
2. Settlement Control: During construction, the settlement amount needs to be continuously monitored. The water - filling rate should match the bearing capacity of the foundation to prevent tank deformation or leakage.
3. Functional Accessories: Equip the tanks with manholes, ventilation valves, emergency cut - off valves, etc. Underground storage tanks also need to be provided with an anti - seepage layer and a drainage system.
V. Industry Solutions
- Chemical Industry: Used for storing corrosive liquids such as acids, alkalis, and strong oxidants. Steel - lined plastic materials are used to avoid chemical reactions.
- Food and Pharmaceutical Industry: Stainless - steel tanks meet the requirements of a sterile environment and are used for storing raw material solutions and pure water.
- Environmental Protection Projects: When dealing with media such as wastewater and oil stains, underground storage tanks can reduce the risk of environmental pollution.
VI. Maintenance and Safety Regulations
Regularly check the sealing of welds, the support status of saddles, and the integrity of the anti - corrosion layer. For underground
storage tanks, special attention should be paid to monitoring the moisture and corrosiveness of the surrounding soil. For flammable and explosive media, anti - static devices need to be installed, and ventilation should be maintained to ensure compliance with national safety standards for storage and transportation equipment.
Through customized design and scientific selection, horizontal storage tanks can efficiently serve diverse industrial scenarios and have become an indispensable storage solution in modern production.